The way people have stored their money has witnessed a remarkable evolution over the years. In the past, the most common method was quite literal and rudimentary - hiding assets under the pillow. This approach, while straightforward, had its glaring drawbacks. In the event of natural disasters like earthquakes or fires, people risked losing everything. This method's lack of security and vulnerability to external factors made it far from ideal.
As society progressed, the concept of banks emerged as a revolutionary solution. People entrusted banks with their money, relying on their promise to secure assets. However, history has shown that banks are not infallible. They often lack transparency, leaving depositors in the dark about the true status of their assets. The question of whether banks genuinely 'hold' the assets or leverage them in other ways has long been a topic of debate and concern.
Thanks to the advent of crypto, users now have the opportunity to keep their funds in self-custody wallets. This marks a significant shift from traditional banking, offering a level of autonomy and control that was previously unavailable. However, not all wallets are created equal. The landscape of digital wallets is diverse, each with its unique features, benefits, and limitations.
Let's take a closer look: has crypto genuinely resolved the issues of trust and transparency that plagued traditional banking? Or are there new challenges and complexities that need to be considered in this modern era of financial management?
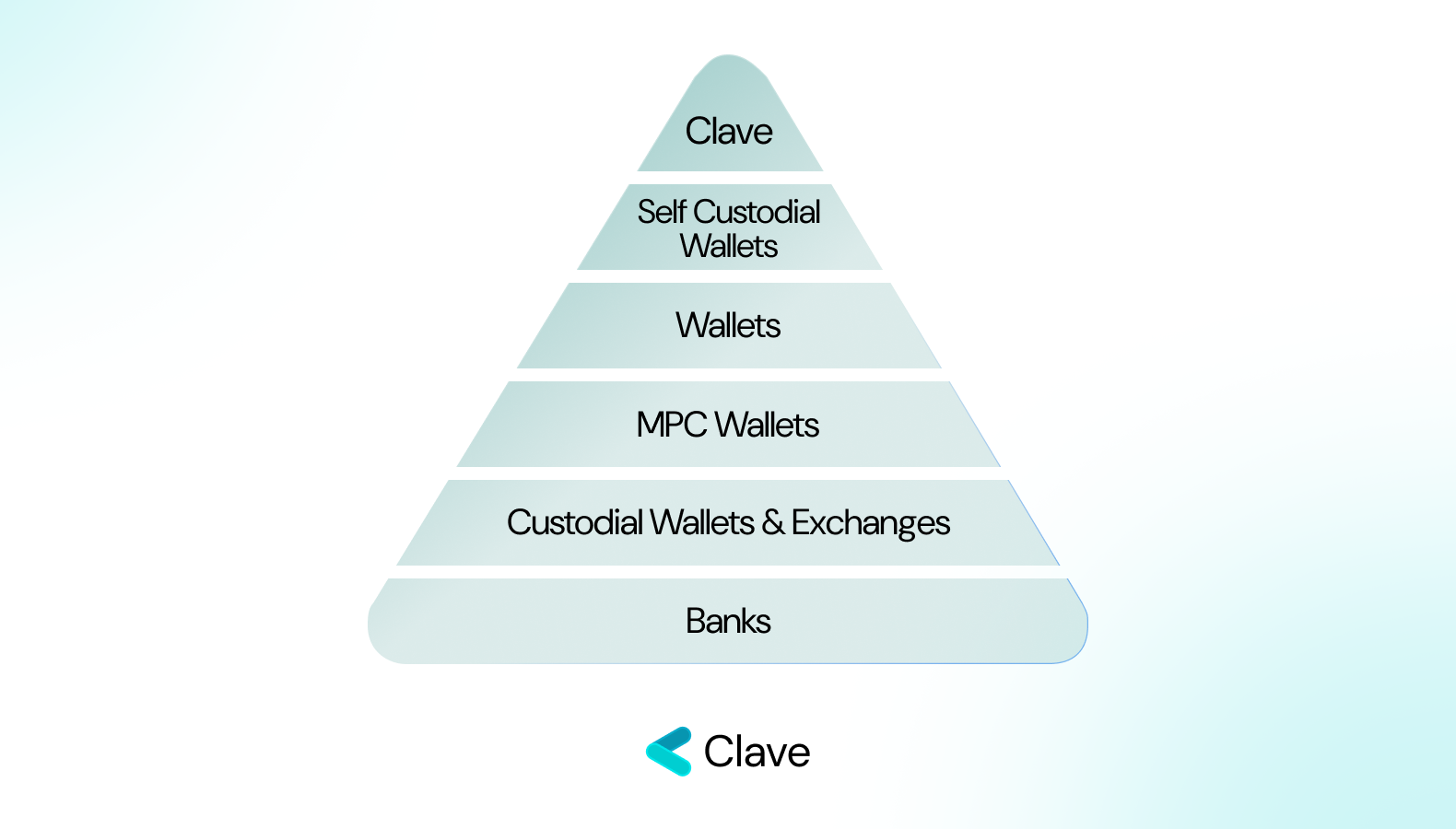
The Lowest Level of Self-Custody: Banks
Nearly everyone has a bank account. It's designed to be simple and user-friendly—though, in reality, the user experience might not always be as smooth as expected (but that's a topic for another day). One of the key advantages of banks is their regulatory compliance, which brings a sense of security and legitimacy. Additionally, the accessibility factor is notable; you can use the money in your bank account virtually anywhere.
However, banks are not without their drawbacks, and a significant one is their lack of transparency. The figures in your account are just that—numbers on a screen. There's no easy way for you to independently verify these numbers. Furthermore, banks have the authority to freeze your funds, sometimes without prior notice, under certain circumstances. This aspect underlines a crucial point: the control you have over the money in your bank account is, to some extent, an illusion. Your access to your own funds can be restricted, making banks a less-than-ideal option for those seeking full custody and control over their assets.
Crypto Exchanges: Bank but with Crypto Functions
Centralized crypto exchanges, often referred to as CEXes, bear a striking resemblance to traditional banks, but with added functionalities tailored to the crypto world. Just like banks, these exchanges can not be audited, leading to a lack of transparency in their operations. This opacity can be a significant concern for users, as there's no straightforward way to verify the safety and integrity of their assets held on these platforms.
Moreover, centralized exchanges hold the power to freeze or, in worst-case scenarios, steal users' funds. This level of control and lack of accountability mirrors some of the most significant drawbacks of conventional banking systems.
However, the key advantage that sets CEXes apart is their crypto-specific functionalities. They enable users to engage in various crypto transactions, such as buying, selling, and sending digital currencies to others. This capability makes them a convenient hub for those looking to participate in the cryptocurrency market, despite the underlying risks similar to those encountered with traditional banks.
Custodial Wallets: Bank but with Transparency
Self-custody refers to having direct control over your financial assets without relying on intermediaries like banks. In the world of digital finance, this means you hold and manage your own private keys, which are necessary to access and control your cryptocurrency. It offers independence from traditional financial systems but requires you to be responsible for the security of your assets. This is where custodial wallets come into play, offering a user-friendly but non self-custodial alternative. These wallets function similarly to banks in that they take on the responsibility of managing your keys, but they come with an added advantage compared to banks: auditability.
Unlike traditional banks, custodial wallets can be audited to verify whether they actually hold the funds they claim to. This feature adds a layer of transparency and trust, aspects that are often missing in conventional banking. While custodial wallets represent the lower end of the self-custody spectrum, they manage to strike a balance between security and user experience. By controlling the keys, these wallets alleviate the burden on the user, simplifying the process of managing digital assets.
In essence, custodial wallets serve as a bridge for those who are not yet ready to take on the full responsibility of self-custody but are seeking more transparency and control than what traditional banks offer.
Semi-Custodial, MPC Wallets: Balancing Trust and Security
While custodial wallets offer ease of use, they lack censorship resistance and create a single point of failure in their centralized system. Crypto's initial goal was to eliminate the need for trust in middlemen, but custodial wallets reintroduce this need by requiring substantial trust in the custodians. This is where MPC (Multi-Party Computation) wallets step in, aiming to distribute trust among various parties, thereby diminishing the reliance on a single custodian.
MPC technology distributes private keys across multiple parties, storing them in different locations. Typically, an MPC wallet will divide the keys into three shards, with the user holding only one of these shards. This setup ensures that even if a user loses their key shard, they can still recover their account. Similarly, in the event of key theft, the distributed nature of the shards mitigates the risk of a single point of failure.
However, this system does introduce an additional layer of trust in the entities that secure the remaining key shards. Given that multiple parties are involved in safeguarding these shards, MPC wallets can be aptly described as 'Semi-Custodial.' They offer a balance between decentralization and security, reducing the dependence on a single entity while maintaining a certain level of trust in the involved parties.
Self-Custodial, EOA Wallets:
Externally Owned Account (EOA) wallets are a solid choice for those seeking complete self-custody. They empower users to store their assets without trusting any third party. However, this high level of autonomy comes with a significant trade-off: the complexity of securely managing 12 words.
Many users find it challenging to securely store these keys, mainly due to a lack of knowledge or understanding of the best practices in digital security. As a result, the user experience in managing keys can be less than ideal, sometimes even daunting. Moreover, the risk of downloading malicious software poses another significant threat. Such software can compromise the security of EOA wallets, leading to the potential theft of the keys.
This combination of factors makes EOA wallets a double-edged sword. On one hand, they offer unparalleled control and independence in managing digital assets. On the other, they demand a high degree of responsibility and vigilance from the user to ensure the security and integrity of their assets.
A New Era for Self Custody with Clave
Clave represents a significant breakthrough in self-custodial solutions, offering an optimal user experience while maintaining full personal custody of assets. At the heart of Clave's innovation is its unique key management approach, which integrates seamlessly with everyday devices.
This approach centers around the use of Passkeys. Passkeys is designed to securely store the keys within a protected area of the user's device, ensuring the safety of sensitive data. One of the most user-friendly features of Clave is the ability to onboard users solely through biometric authentication. This method not only enhances security but also simplifies the process, making it more accessible.
Moreover, passkeys provide an additional layer of security. They keep the user's keys safe even in the event of a device compromise, offering peace of mind and enhanced protection. Alongside this, Clave's key management system works with various recovery methods. These methods ensure that users can regain access to their wallets, even if their primary devices are lost or damaged.
Ultimately, Clave's vision is to empower users with complete control over their assets. It achieves this by leveraging the capabilities of modern devices and removing the need for key storage, all while delivering a superior user experience.
About Clave
Clave is an easy-to-use, non-custodial smart wallet powered by Account Abstraction and the hardware-level security elements (e.g., Secure Enclave, Android Trustzone, etc.) to simplify the onchain experience for the next billions. By empowering users with a user-friendly and secure bridge to seamlessly integrate their assets into everyday life, Clave delivers a comprehensive fintech solution, ensuring a holistic financial experience for all.
Connect with Clave:
- Website: https://www.getclave.io/
- Twitter: https://twitter.com/getclave
- LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/getclave/
- Farcaster: https://warpcast.com/getclave
- Marketing inquiries: marketing@clave.team
- Mail: info@clave.team


